In today’s fast-paced digital world, traditional banking is undergoing a significant transformation. One of the most prominent changes is the rise of digital banks. But what exactly is a digital bank? This article will explore the definition of a digital bank, differentiating it from traditional banks and online banking services. We’ll delve into the core functionalities and features that characterize a digital bank, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of adopting this modern approach to financial management. Understanding the workings of a digital bank is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the evolving landscape of personal finance.
Digital banks offer a compelling alternative to traditional brick-and-mortar institutions, providing a range of services accessible entirely online. From opening an account to applying for a loan, digital banking streamlines financial processes, often with lower fees and higher interest rates on savings accounts. We will examine the mechanics of how a digital bank operates, including its reliance on technology, security measures, and regulatory compliance. This comprehensive overview will equip you with the knowledge necessary to determine if a digital bank is the right choice for your financial needs. By understanding the benefits and potential drawbacks of digital banking, you can make informed decisions about your financial future.
Definition of a Digital Bank
A digital bank, sometimes referred to as a virtual bank or an online bank, is a financial institution that delivers banking services primarily, or exclusively, through digital channels such as mobile apps and online platforms. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar banks, digital banks do not operate physical branches, allowing them to offer services 24/7 and often at lower costs.
They provide a wide range of banking services, including account opening, money transfers, bill payments, and loan applications, all managed electronically. While some digital banks are divisions of established traditional banks, others operate independently as fully licensed institutions.
Differences from Traditional Banks
Digital banks distinguish themselves from traditional banks in several key ways. One primary difference is physical presence. Traditional banks operate through a network of brick-and-mortar branches, while digital banks primarily exist online, without physical locations.
Another key difference lies in account access and management. Digital banks offer 24/7 account access through online platforms and mobile apps, providing greater convenience and flexibility. Traditional banks typically offer limited online functionality and require customers to visit branches for certain transactions.
Fees are another area of divergence. Digital banks often have lower or no monthly maintenance fees, overdraft fees, and minimum balance requirements, making them a more cost-effective option for some customers. Traditional banks generally have more fees associated with their accounts.
How Digital Banks Operate
Digital banks operate primarily through online platforms and mobile applications. They leverage technology to automate processes, reducing the need for physical branches.
Account opening, money transfers, bill payments, and customer support are typically handled digitally. Automated systems manage transactions, often leading to lower operational costs compared to traditional banks.
Security is a crucial aspect of digital banking operations. Multi-factor authentication, data encryption, and fraud detection systems are implemented to protect customer information and funds.
Some digital banks partner with traditional banks for certain services, like ATM access or check deposits. However, core banking functions remain primarily digital.
Benefits for Consumers
Digital banks offer several advantages over traditional banking institutions. Convenience is a key factor, with 24/7 account access and mobile banking capabilities allowing for transactions and balance checks anytime, anywhere.
Lower fees are another significant draw. Digital banks often have lower overhead costs, which can translate to reduced or eliminated monthly maintenance fees, overdraft charges, and ATM fees.
Higher interest rates on savings accounts are also a common benefit. Due to their lower operating costs, digital banks can often offer more competitive interest rates compared to traditional banks.
Innovative features are often a hallmark of digital banks. These can include budgeting tools, automated savings features, and personalized financial management advice.
Speed and efficiency are also improved with digital banks. Account opening is typically quick and easy, and transactions are often processed faster than with traditional banks.
Examples of Popular Digital Banks
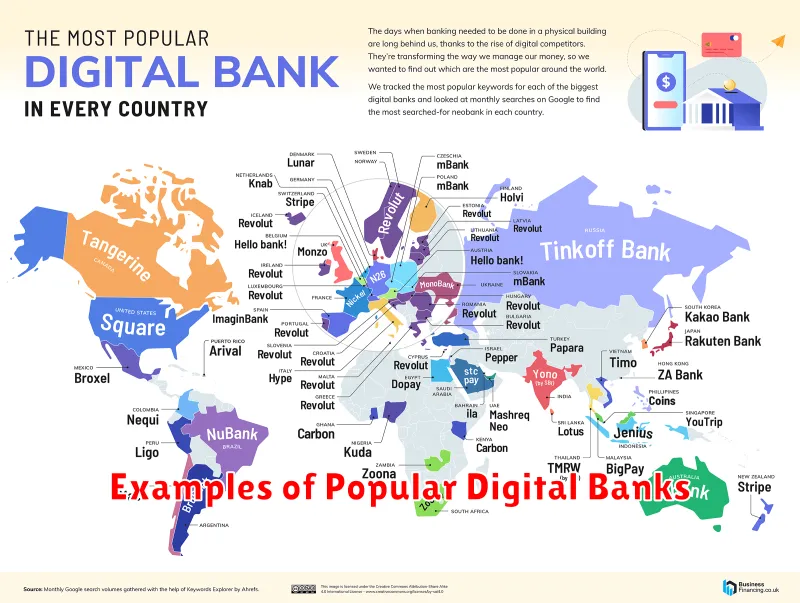
Several digital banks have gained prominence in recent years, offering a range of services and catering to various customer needs. It’s important to note that the availability and popularity of these banks can vary by region.
In the United States, some popular examples include Chime, known for its fee-free overdraft and early direct deposit features; Varo Bank, offering high-yield savings accounts and no-fee checking; and Current, focusing on faster payments and budgeting tools.
Internationally, digital banks like Revolut and N26 have gained significant traction, offering multicurrency accounts and international money transfers. Monzo, primarily based in the UK, is another prominent digital bank focusing on user experience and budgeting features.
These examples represent a small portion of the growing digital banking landscape. It’s important to research the specific features and offerings of each bank to determine which best suits your individual financial needs.

