In today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, choosing the right banking institution is more critical than ever. Consumers are faced with a plethora of options, ranging from established traditional banks to innovative digital banks. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of digital banks vs traditional banks, outlining the key differences in services, fees, accessibility, and security to help you make an informed decision. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each banking model is crucial for selecting the best fit for your financial needs and preferences. Whether you prioritize physical branches, personalized customer service, or cutting-edge technology and lower fees, this comparison will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the modern banking world.
This detailed comparison will delve into the core functionalities of both digital banks and traditional banks. We will explore the benefits and drawbacks of each, examining factors such as online banking capabilities, mobile banking accessibility, interest rates on savings accounts and loans, ATM access, customer service availability, and overall security measures. By analyzing these crucial aspects, we aim to clarify the distinctions between digital banks vs traditional banks and empower you to choose the banking solution that best aligns with your individual financial goals and lifestyle.
Overview of Banking Models
This section provides a brief overview of the two primary banking models: traditional banking and digital banking. Understanding their core functionalities and operational differences is crucial for a comprehensive comparison.
Traditional Banking
Traditional banks operate primarily through a network of physical branches. Customers perform transactions, access services, and receive financial advice in person. These banks have established infrastructure and regulatory oversight, often prioritizing personal relationships and face-to-face interactions. Their services are typically delivered during standard business hours.
Digital Banking
Digital banks, also known as neobanks or virtual banks, operate primarily online. They leverage technology to provide 24/7 access to banking services through websites and mobile applications. These banks often emphasize convenience, automation, and lower fees. Reduced overhead from the absence of physical branches allows them to offer competitive interest rates and other incentives.
The following table summarizes the key characteristics:
| Feature | Traditional Bank | Digital Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Operation | Physical Branches | Online/Mobile Platforms |
| Accessibility | Limited by Business Hours | 24/7 |
| Customer Interaction | In-Person/Traditional Channels | Digital/Automated |
Service Accessibility
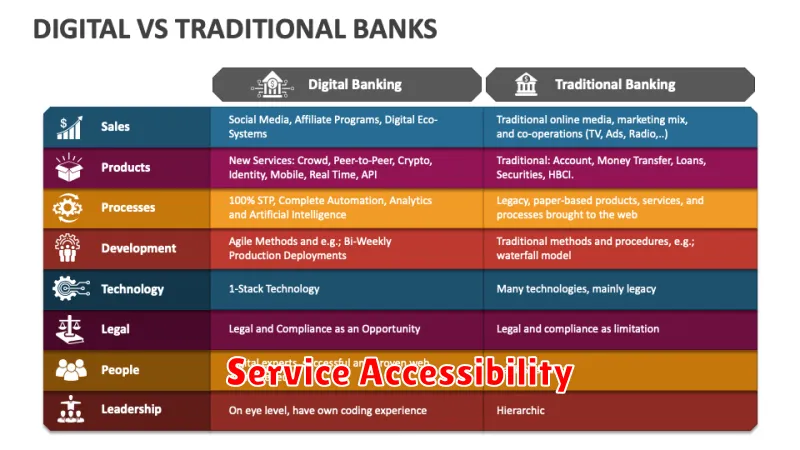
A key differentiator between digital and traditional banks lies in service accessibility. Digital banks operate primarily online, offering 24/7 service availability through websites and mobile applications. This allows customers to manage their finances anytime, anywhere, without being limited by branch operating hours.
Traditional banks, while increasingly adopting digital services, still rely heavily on physical branch networks. This offers in-person support and personalized service, which some customers prefer. However, access is restricted to branch locations and their operating hours, potentially creating inconvenience for customers with busy schedules or those located far from a branch.
| Feature | Digital Bank | Traditional Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Access | 24/7 online and mobile | Limited by branch hours and location |
| Support | Primarily online/phone support | In-person and online/phone support |
Cost and Fees Differences
A key differentiator between digital and traditional banks lies in their cost structures, which directly impact the fees passed on to customers. Digital banks, operating with lower overhead due to the absence of physical branches, often offer lower or no fees for services like monthly maintenance, ATM withdrawals (sometimes through partnerships), and overdraft protection.
Traditional banks, burdened by the costs of maintaining branches and a larger workforce, typically charge higher fees for these same services. They may offer fee waivers based on minimum balance requirements or other criteria, but these may not be accessible to all customers.
| Feature | Digital Banks | Traditional Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Maintenance | Often Free | Potentially High, May be Waived |
| ATM Fees | Often Free (Partner Network) | Can be High, Especially Out-of-Network |
| Overdraft Fees | Potentially Lower or No Fee Options | Generally High |
Technology and User Experience
A key differentiator between digital and traditional banks lies in their approach to technology and the resulting user experience. Digital banks, built from the ground up on modern technological infrastructure, prioritize a seamless and intuitive digital experience. Mobile-first design is paramount, offering customers convenient access to banking services anytime, anywhere.
Traditional banks, while adapting to digital trends, often grapple with legacy systems. This can lead to a less streamlined online and mobile experience compared to their digital counterparts. While they are investing in modernization, the transition can be complex and time-consuming.
Key features typically offered by digital banks include robust mobile apps, personalized financial management tools, and 24/7 customer support via chat or email. Traditional banks are catching up, but digital banks often lead in innovation and speed of implementation for new features and services.
Which One Suits You Best?

Choosing between a digital bank and a traditional bank depends entirely on your individual needs and preferences. There is no single “best” option, only the right fit for you.
Consider your tech savviness. Are you comfortable managing your finances entirely through an app? If not, a traditional bank with physical branches might be a better choice. Think about your accessibility needs. Do you require in-person services, or are you comfortable with online and phone support?
Fees are another crucial factor. Digital banks often boast lower fees, but examine the details carefully. Some traditional banks offer fee waivers that might make them more cost-effective in the long run. Finally, assess your comfort level. Are you comfortable entrusting your finances to a newer institution, or do you prefer the established security of a traditional bank?
| Feature | Digital Bank | Traditional Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Primarily online and mobile | Physical branches and online |
| Fees | Generally lower | Potentially higher, but waivers may apply |
| Technology | Cutting-edge features and apps | Varying levels of technological adoption |
| Customer Service | Primarily online and phone support | In-person, online, and phone support |